Results were found under videos, presentations, posters, papers .
There are no videos within this category so far.

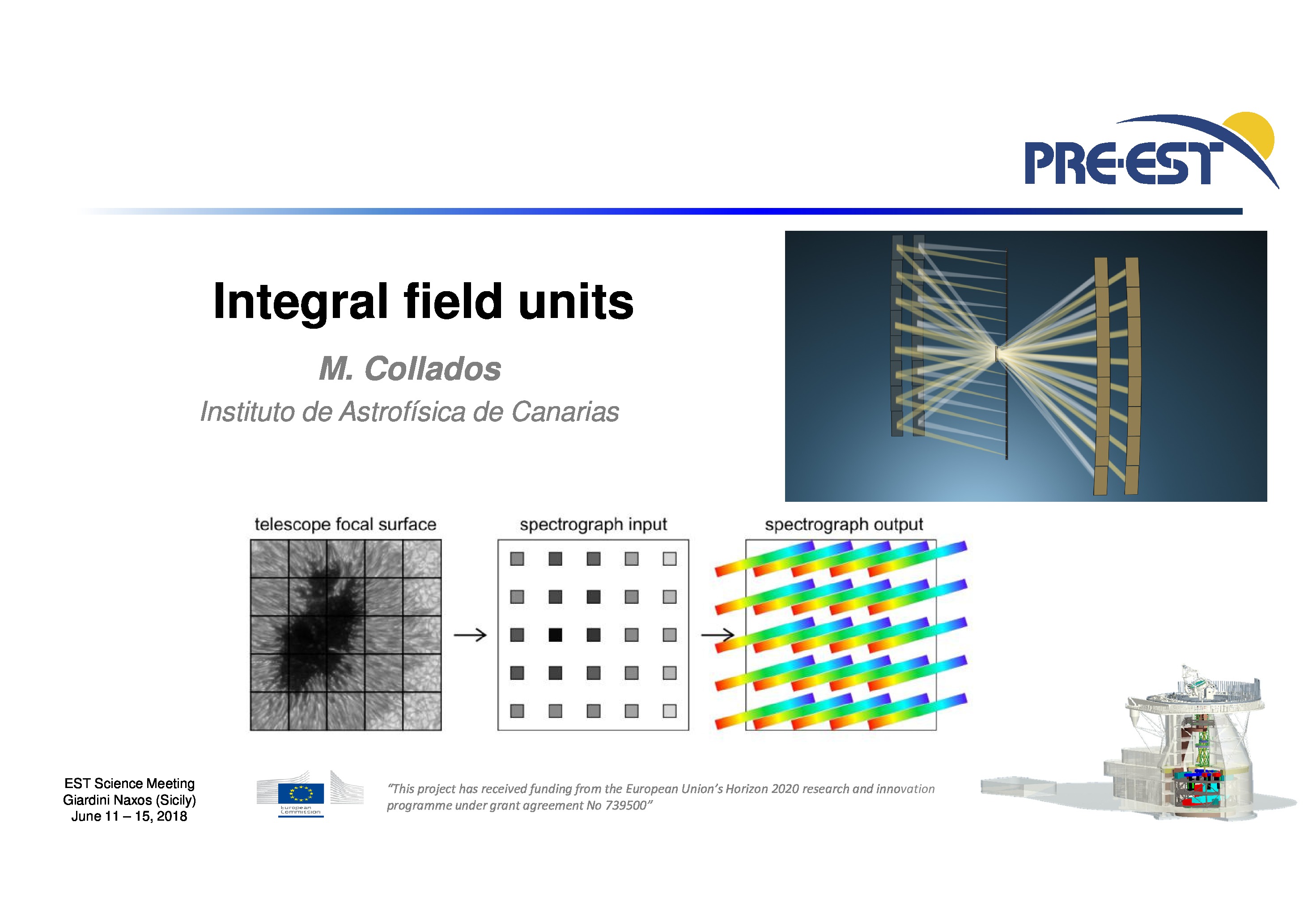







There are no posters within this category so far.
There are no papers within this category so far.